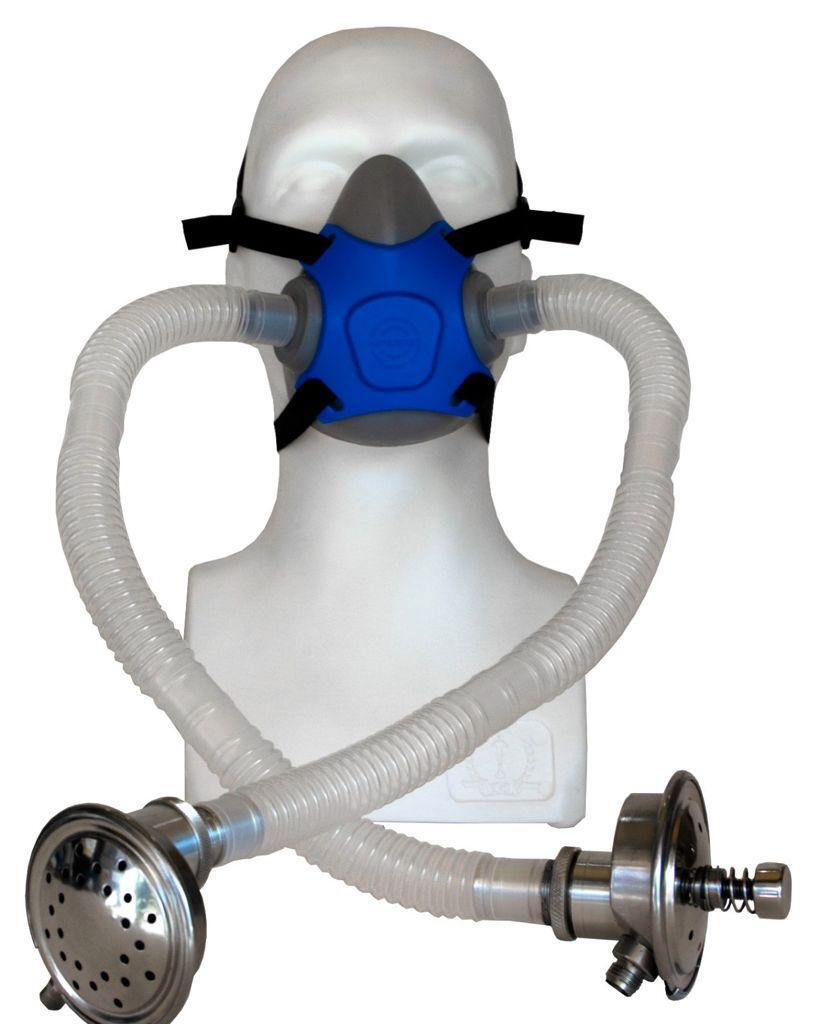
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is the systemic delivery of oxygen inside the hyperbaric chamber at values greater than atmospheric pressure. In short, you breathe 95% pure oxygen through the oxygen mask while the body is exposed to elevated ambient pressures, up to 2.0 ATA.

Time to take a dive.
The HBOT session starts with gradually increasing pressure inside the hyperbaric chamber. This is called a ‘dive’, similar to gently descending underwater. At 2.0 ATA (the working pressure of HPOD UNO) the pressure is equivalent to being approximately 10 meters (or 32.8 feet) deep underwater.
Take a deep breath of pure oxygen.
While the pressure is raised, you breathe pure oxygen through the breathing mask or the BIBS system (Breathe-In-Breathing System). The working mechanism behind Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is based on the principles of gas dissolution and the way oxygen is transported and processed in the body through the circulatory system.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a major upgrade for your health strategy.
To build a solid foundation for good health and vitality, start with the very basics – optimal oxygen intake.
The primary therapeutic mechanism of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is based on its ability to enhance the oxygenation of tissues by breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment.
Oxygen delivered under the right pressure brings effective results.
This increased pressure allows the lungs to take in a higher concentration of oxygen, which is then dissolved into the bloodstream and distributed throughout the body.
Oxygen is a natural medicine.
Oxygen is essential for life, cellular metabolism, and all healing processes. Every cell in our body requires oxygen to function and produce energy. In the air we breathe every day there is about 21% oxygen and 79% percent nitrogen. Our bodies only take in about 5% of oxygen from that total in each inhalation.
More pressure, more available oxygen
The increased atmospheric pressure within a hyperbaric chamber will enhance the amount of oxygen dissolved in bodily fluids, particularly the plasma and cerebral spinal fluid.
More dissolved oxygen in tissues, more reach to injury sites
The dissolved oxygen can reach tissues and organs that might have compromised blood flow or oxygen supply due to injury, inflammation, or certain medical conditions.
More oxygen, more reach, better chances of healing
Elevated oxygen levels can aid in healing wounds, reducing inflammation, promoting tissue repair, and supporting the body’s natural healing processes.
How do our bodies process oxygen?
After inhalation, the oxygen we take in travels to our alveoli. This is the place where primary gas exchange occurs. With the help of the pulmonary capillaries, oxygen is diffused into our bloodstream. From there it bonds to the haemoglobin in our blood and is distributed to all parts of our bodies through the circulatory system.
The circulatory system
Cells traveling through the bloodstream depend on circulation in order to deliver oxygen to vital organs. During severe cases of trauma, the system clots and is restricted, creating a ‘traffic jam’ for blood cells. This inefficient flow is the main cause of organ-brain damage, critical disablement, or death.
How does hyperbaric oxygen therapy work?
Higher oxygen levels contribute to tissue repair, can reduce tissue damage caused by insufficient oxygen supply (such as in wounds or injuries), and improve the body’s well-being.
HBOT helps deliver supplemented levels of oxygen to cells, tissues and organs at higher pressure. The procedure aims to empower the body’s natural healing processes, reduce inflammation, and sustain the growth of new blood vessels.

What happens when the body is flooded with more oxygen?
An increase in the concentration of oxygen in the blood facilitates enhanced cellular oxygenation. This accelerates wound and injury healing and also produces anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, high oxygen levels can inhibit the growth of certain anaerobic bacteria, providing bactericidal benefits.
Why does the body need oxygen?
Oxygen sustains life, it’s the necessary element for the optimal functioning of cells, tissues, and organs. Cells convert nutrients into energy through the process of cellular respiration.
This energy is used to fuel all bodily functions and activities like supporting metabolism, growth, and body maintenance. Oxygen supports the immune system, facilitates the elimination of waste products, and is necessary for brain function and cognitive processes.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a vital process where cells transform nutrients, such as glucose, into energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through complex reactions.
Primarily occurring in the mitochondria, often referred to as the cell’s powerhouse, this energy conversion also produces byproducts like carbon dioxide and water, which the body expels through respiration and other means.
This process is essential for powering various bodily functions and maintaining consistent energy levels.
Exploring the mechanisms of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
When the HPOD MONO chamber is pressurized to 1.6 ATA, the body feels a weight equivalent to approximately 16,848 pounds per square inch (psi). This pressure exerts its effects on the body, leading to various physiological responses that are beneficial in hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
This pressure-induced mechanical impact on the body starts to reduce edema, countering the swelling that hampers oxygenation. By diminishing edema, blood flow surges, infusing insult sites with an abundance of oxygen for accelerated healing.